Understanding Orphan Pages
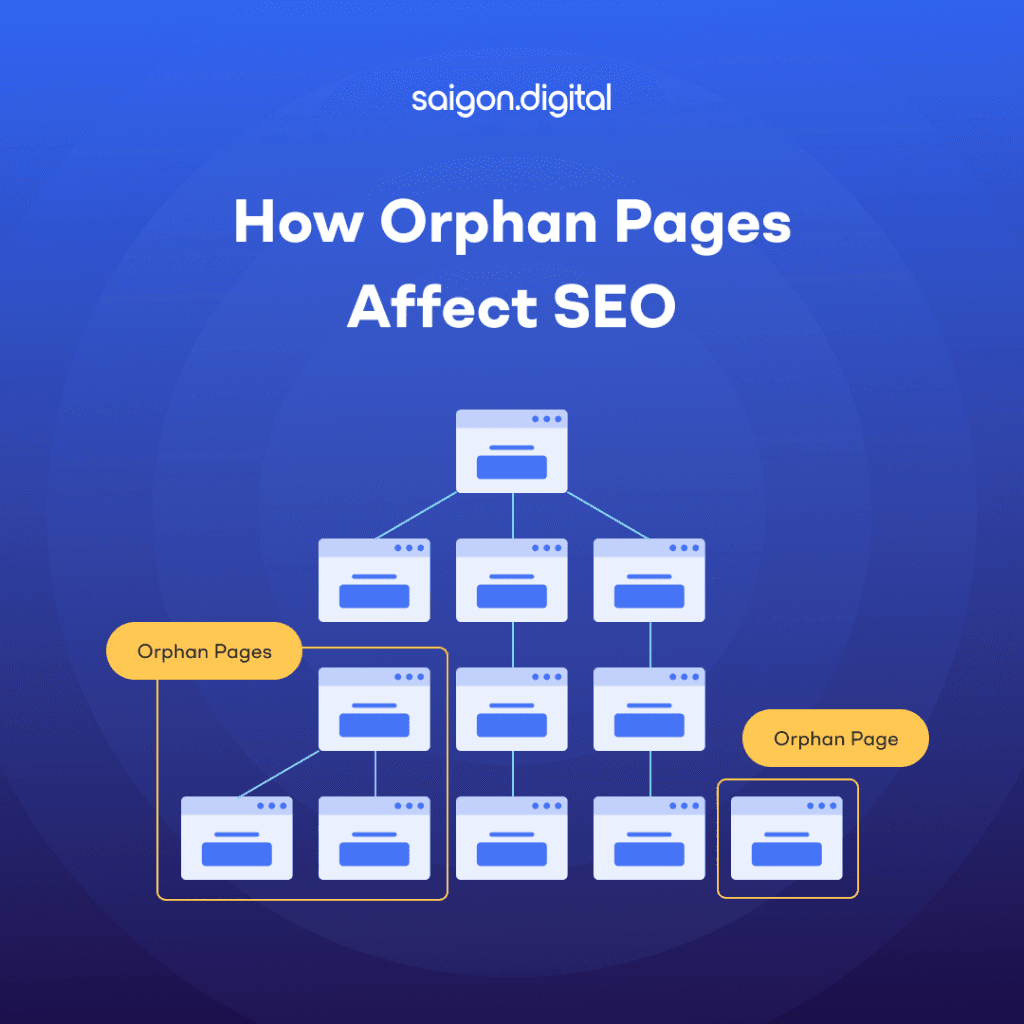
An orphan page is a web page that lacks incoming internal links, making it inaccessible through the website's navigation. These pages can only be visited via external backlinks or direct URLs. While some pages are intentionally orphaned, such as certain guides or advertising landing pages, accidental orphan pages can harm your SEO efforts and require attention.What is the Difference Between Orphan Pages and Dead-End Pages?
Orphan Pages
Orphan pages have no incoming internal links, making them inaccessible from other parts of the website. Users might visit them through external links or direct URLs, but they won't easily find them through internal navigation. This can lead to poor indexing and user experience.
Dead-End Pages
Dead-end pages, on the other hand, have incoming links but lack outgoing links to other pages within the same site. Visitors and search engine crawlers can access these pages but cannot navigate further, which wastes potential traffic and reduces overall site engagement.Orphan pages and dead-end pages are opposites. Orphan pages lack incoming links, preventing access, while dead-end pages have no outgoing links, trapping visitors on a single page. You need to address both issues to improve SEO and enhance user experience.How Orphan Pages Affect SEO
1. Page Does Not Get Indexed
Search engine crawlers rely on internal links to find and index pages. Without these links, orphan pages remain invisible to crawlers, preventing them from being indexed and appearing in search results. While XML sitemaps can help, internal links are crucial for proper indexing.2. Wasting Crawl Budget
Search engine crawlers have a limited amount of time to explore websites. If too much of that time is wasted on low-value, orphan pages, there’s less focus on more important content. This can lead to delays in indexing new pages and may harm your site’s overall visibility.
3. Poor Search Rankings
Pages without internal links lack the link equity needed for higher search rankings. Google's PageRank algorithm values inbound links as indicators of quality and authority. Without these links, orphan pages may struggle to rank well and attract organic traffic.
4. Poor User Experience
Orphan pages are virtually invisible to visitors who navigate through menus and links. This limits user access to potentially valuable content, leading to a poor user experience. Ensuring all pages are accessible through navigation improves usability and content discoverability.
How to Identify Orphan Pages
1. Compile a Complete List of Your Website's Pages
Begin by gathering a full list of all the pages on your site. Simply pointing your website crawler at the homepage won’t help, as orphan pages, by definition, lack internal links. You’ll need to manually feed the crawler a comprehensive list of URLs. You can obtain this list by:- Using your sitemap: Ensure your sitemap is up-to-date and contains all site URLs.
- Exporting a list from your CMS: Some platforms, like WordPress, allow you to export a CSV file of all your URLs.
- Use SEO Tools: Tools like Google Search Console, Screaming Frog, or Ahrefs can identify pages with no inbound internal links.
2. Conduct a Website Crawl
Set up the crawler to scan your entire website, focusing on internal links. Specify the starting point (usually your homepage) and any desired depth or exclusions.
This will help you quickly pinpoint orphan pages. Schedule recurring audits to ensure the new ones don’t go unnoticed as your site evolves.
3. Review the Audit Results
Once the crawl is complete, examine the results to identify any orphan pages.- Assess Page Relevance: Determine if they are still relevant to your website's goals and content strategy. Consider their age, topic, and alignment with your overall messaging.
- Evaluate Traffic and Engagement: Use web analytics tools to analyze traffic sources, page views, and user behaviour for each orphan page. This will help you understand if they are still valuable or if they can be removed.
- Identify Potential Reasons: Explore why these pages might have become orphaned. This could be due to changes in website structure, outdated content, or simply an oversight.
4. Regularly Rerun Audits
As your website grows and changes, new orphan pages may appear, so it’s crucial to schedule regular audits. Set up automated crawls to stay on top of any new issues.
How to Fix Orphan Pages
There are two main types of orphan pages expected orphan pages and unexpected ones.
1. Expected Orphan Pages: Not Typically a Concern
After running a site crawl and comparing it with server logs, you’ll identify pages that Google finds but that aren't linked within your site’s structure. Many of these will fall into the following categories:- Pages Linked from External Sites: If another website links to a page you've removed or redirected, Google might still find it. Since you don’t control external links, reach out to the site owner and ask them to update the link to the correct URL.
- Pages with Non-200 Status Codes: Google may continue to crawl pages with temporary errors (like 4xx status codes) even after they're corrected. There's no need to worry – Google will eventually stop crawling them.
- Expired Pages: Websites with short-lived content (e.g., classifieds) often have a high turnover of expired pages. You only need to be concerned if these pages remain orphaned for a long period. Otherwise, they simply reflect your site’s content turnover.
2. Unexpected Orphan Pages: Pay Attention
- Expired Content with Active Links: Remove expired content or ensure it returns a 404 or 410 status code.
- Pages Left Out of Migration: Redirect old URLs to their new counterparts or return a 404 or 410 status code.
- Sitemap Syntax Errors: Correct any syntax errors in your sitemap to prevent erroneous URLs.
- Canonical Tag Errors: Ensure canonical tags are correctly set up to avoid duplicate content issues.
- Important Pages Missing Links: Regularly review your website's structure to ensure all important pages are linked.
Conclusion
Orphan pages can hinder your SEO efforts by reducing the visibility and accessibility of your content. By identifying and fixing these pages, you enhance your site’s usability, improve user experience, and ensure better link equity distribution. Regular audits and a strong internal linking strategy are essential in managing these pages effectively.Ready to improve your site's SEO and user experience? Schedule a call with Saigon Digital today and let our experts help you achieve your digital goals.FAQs About Orphan Pages
1. What are orphan pages in SEO?
Orphan pages are web pages that have no internal links pointing to them, meaning they can’t be accessed through your site’s navigation. They are only reachable through external backlinks or direct URLs. While sometimes intentional (like campaign landing pages), unintentional orphan pages can harm SEO performance.
2. How are orphan pages different from dead-end pages?
- Orphan pages have no incoming internal links, making them invisible in site navigation.
- Dead-end pages have no outgoing links, trapping users and crawlers on a single page.
Both issues negatively impact SEO and user experience, so they should be addressed.
3. Why are orphan pages bad for SEO?
Orphan pages hurt SEO because:
- They may not get indexed by search engines
- They waste crawl budget
- They lack link equity, making it hard to rank
- They create poor user experiences since visitors can’t easily find them
4. How can I find orphan pages on my website?
You can identify orphan pages by:
- Compiling a complete list of URLs from your sitemap or CMS
- Using SEO tools like Google Search Console, Screaming Frog, or Ahrefs
- Running a full website crawl and comparing it with your list of URLs
- Conducting regular audits to catch newly created orphan pages
5. What are the best ways to fix orphan pages?
To fix orphan pages, you can:
- Add internal links from relevant pages to connect them
- Redirect outdated or irrelevant orphan pages to more valuable content
- Remove expired or low-value pages with a 404/410 status code
- Fix sitemap or canonical errors that may cause pages to be excluded
- Regularly audit your site structure to ensure important pages remain accessible





