
Understanding Scalability in Web Development
Scalability in web development involves two key approaches: vertical scaling and horizontal scaling.
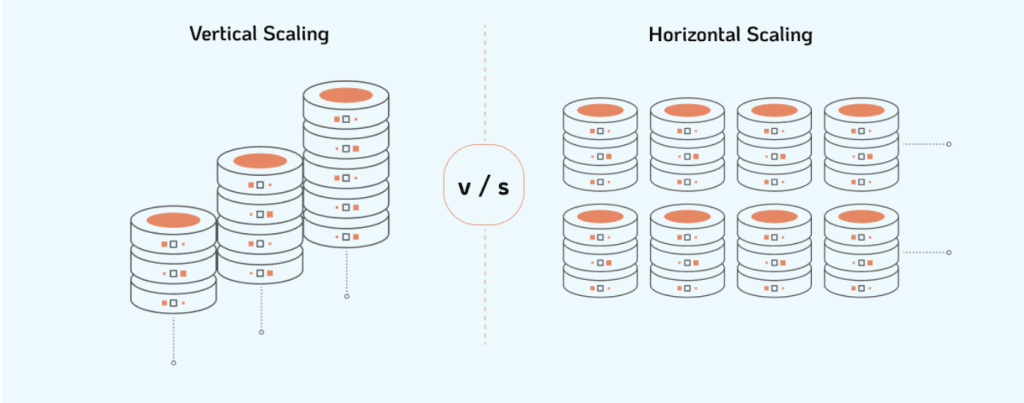
- Vertical Scaling: Vertical scaling, or scaling up, entails increasing the capacity of individual components, like upgrading hardware resources such as CPU or RAM on a single server. While simple to implement, it has limits and may lack redundancy.
- Horizontal Scaling: Horizontal scaling, or scaling out, spreads the workload across multiple servers or nodes. This approach offers greater scalability and fault tolerance but requires managing distributed systems.
Architectural Patterns for Scalability
Scalable architectural patterns such as microservices, serverless, and distributed systems enable flexible and resilient web applications. Microservices promote modularity and independence, while serverless architectures offer on-demand scalability and cost-efficiency. Distributed systems leverage the power of multiple nodes to handle increased loads and ensure fault tolerance.
Database Scalability Strategies
Database scalability is crucial for managing growing data volumes and increasing operations efficiently. Here are some key strategies:- Sharding: Partition data across multiple database instances based on a key. This improves scalability by distributing the workload, but it also adds complexity.
- Replication: Create copies of data across multiple servers to distribute read queries and improve fault tolerance. However, it doesn't directly address scalability.
- Partitioning: Divide large tables or indexes into smaller partitions for parallel processing and better query performance. It requires careful planning.
- Caching: Store frequently accessed data in memory to reduce database queries and improve read scalability. Challenges include cache invalidation and data consistency.
- Denormalisation: Restructure the database schema to reduce complex joins and improve query performance. This can speed up read operations but may increase storage requirements.
Scalable Infrastructure and Deployment
Reliable performance and the ability to accommodate increasing user demands depend on a scalable infrastructure. The following are important deployment and infrastructure scalability strategies:- Cloud Computing Platforms: Utilise cloud services such as AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud for scalable infrastructure. These platforms offer on-demand resources, auto-scaling capabilities, and global availability zones to handle fluctuating workloads efficiently.
- Containerisation and Orchestration: Deploy applications consistently using Docker, managed with Kubernetes for automated scaling and load balancing.
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC): Provision and manage infrastructure programmatically with tools like Terraform for consistency and scalability.
- Auto-scaling and Load Balancing: Configure auto-scaling policies to dynamically adjust resource allocation based on workload demands. Load balancers distribute incoming traffic across multiple instances or containers, ensuring high availability and scalability while minimising downtime.
- High Availability and Disaster Recovery: Ensure continuous availability with redundant architectures, data replication, and disaster recovery mechanisms across multiple regions or availability zones.





