
What is AI Optimisation in SEO?
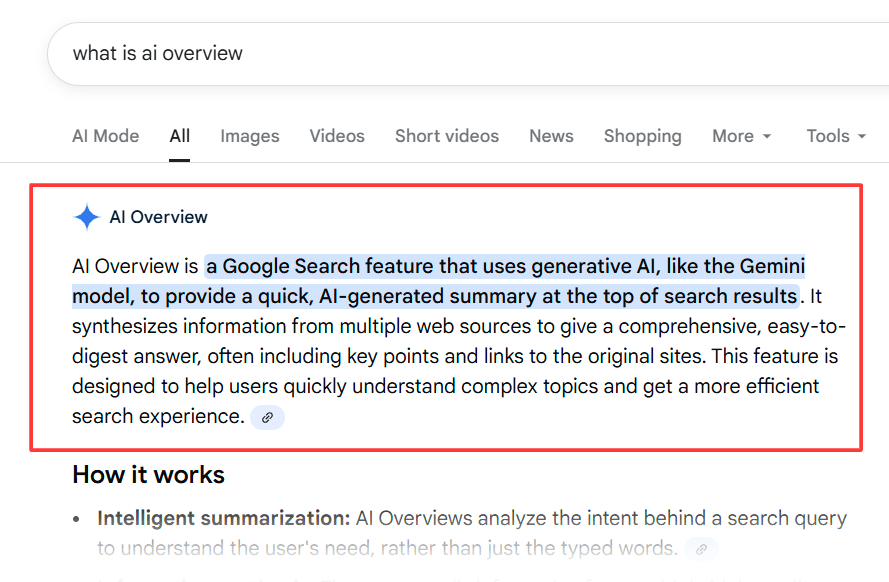
“AI optimisation” (sometimes called AI SEO, AIO, or generative engine optimisation) refers to the practice of adjusting and structuring your content, site, and signals so that AI systems can discover, interpret, and prefer to cite or include your content when they generate answers for users. In the traditional SEO world, you optimise for Google, Bing, or other search engines to rank pages in organic listings (SERPs) based on relevance, authority, and user signals. But as AI-driven answer engines (e.g. conversational assistants, “ AI Overviews ,” large language model–backed search interfaces) grow in prominence, you also want your content to be selected and surfaced in AI-generated responses. That’s where AI optimisation comes in. Some related terms you might see:- AI SEO / AIO: Using AI tools and practices to optimise content and SEO workflows, and to ensure your content is visible to AI systems.
- Generative Engine Optimisation (GEO): A subset of AI optimisation that focuses on being cited or used in generative AI outputs (e.g. ChatGPT, Google’s Search Generative Experience).
- Answer Engine Optimisation (AEO): Optimising content so that AI-powered answer engines (or assistants) can present direct answers (snippets, QandA) to users.
Why AI Optimisation Matters Now (and in the Future)
The widespread usage of AI in the hands of everyday people has never been more prominent ever since ChatGPT was introduced. Since then, the technology and the way people utilise it has changed and evolved rapidly. AI optimisation is starting to be and would continue to be in the forefront of every businesses’ minds.The Shift in How Users Get Answers
Increasingly, users are turning not just to search engines, but to conversational AI agents (e.g. chatbots, voice assistants, AI summarisation features) to get responses. These systems often synthesise information from multiple sources rather than simply returning a ranked list of links. As a result:- Even if your page ranks well in traditional search, it might not be included in the AI-generated answer or summary.
- AI systems may cite other pages as sources, giving them indirect authority and traffic referral.
- The “click-through” dynamic changes: content that gets cited or summarised in AI may attract users’ attention without needing them to click deep into SERPs.
Preserving Relevance and Visibility
Without AI optimisation, your content may become less visible in emerging search/answer paradigms. To maintain and grow visibility:- You want AI systems to recognise your content as credible and authoritative.
- You want to structure content so that AI tools can parse and extract the key parts (e.g. definitions, lists, tables).
- You want to match how AI systems interpret and generate responses, not just how search engines rank pages.
The Beginner’s Foundation: Getting Started with AI Optimisation
If you’re new to this, here is a step-by-step approach:1. Start with Solid SEO Fundamentals
Before layering AI optimisation, ensure your site is technically healthy:- Good site speed, mobile responsiveness, clean architecture, proper indexing.
- Use schema markup (structured data) to help machines understand content context (for example FAQ schema, article schema, QandA, etc.).
- Well-written, user-friendly content with clear headings, structured paragraphs, lists, images.
2. Use AI Tools Wisely in Your Workflow
You can already benefit from AI in your SEO work since AI can help you with the following tasks:- Keyword research + topic ideation: Use generative tools to expand your seed keywords, find long-tail related ideas, or explore conversational phrasing.
- Content outlines / gap analysis: Let AI examine top-ranking pages and help you outline content that fills gaps or improves depth.
- Optimising on-page content: Use AI to suggest internal linking opportunities, secondary keywords, paragraph restructuring or meta descriptions.
- Refreshing old content: Ask AI to compare your content to newer sources, suggest updates, or detect outdated information.
3. Frame Content to Answer Questions Directly
Since AI systems often extract short direct answers (snippets), you want your content to:- Introduce the answer early (e.g. the core definition or key point in the first paragraph).
- Use clear headings, question-answer format (e.g. “What is …?”, “Why does … matter?”).
- Use bullet points, numbered lists, tables to structure information.
- Include relevant examples, case studies, statistics, and citations.
4. Build Authority and Trust Signals
AI systems tend to favour sources with credibility. To improve your chances:- Use accurate, up-to-date citations and link to reputable external sources.
- Show expertise: include author bios, credentials, case examples.
- Use consistent branding and domain authority (backlinks still matter).
- Encourage content sharing and mentions, as AI systems often pick up on signals of “earned media.”
Advanced Strategies in AI Optimisation (for SEO + Generative Visibility)
Once you have the basics in place, here are more sophisticated techniques to gain advantage:1. Optimise for GEO (Generative Engine Optimisation)
GEO is specifically about being cited by generative AI systems (e.g. ChatGPT, Perplexity, Gemini). Key tactics include:- Machine-friendly cues: Use cues that signal to AI systems what is important such as labelled sections, bold/highlighted key sentences, summaries.
- Support with evidence: Use data, quotes, external sources since AI systems prefer “verifiable” content over vague statements.
- llms.txt or AI-specific metadata: An emerging idea is to include a file akin to robots.txt for large language models, letting them know what content is preferred for citations. (This is still experimental however.)
- Content freshness and diversity: Generative engines favour up-to-date content; updating regularly increases your chance of being cited.
- Language strategies: Use variant phrasings, synonyms, question forms because generative engines may match queries in many forms.
2. Intent Modelling and Role-Based Structuring
Recent research suggests content should be shaped around intent roles (e.g. “definition”, “comparison”, “how-to”, “example”) so that generative engines can map content sections to the query’s “role”. Practically, make sure you:- Break your content into roles, e.g. a “definition” section, then “benefits”, then “step-by-step”, then “case studies”.
- Signal those roles with headings (H2/H3) and use phrasing aligned with common query intents.
- This gives AI systems a clearer structure to “pull” relevant sections when generating answers.
3. Multi-Engine and Language-Aware Optimisation
Generative engines are not all the same: ChatGPT, Bing Chat, Google SGE, Perplexity, Gemini behave differently in terms of how they select content and weigh signals. Therefore, consider doing the following to increase your chance of being cited on different AI engines:- Track which platforms your content is being referenced in.
- Tailor part of your phrasing or structure to the quirks of each engine (if possible).
- Use multilingual versions with appropriate optimised structure if you target multiple languages, generative systems may pick cross-language sources.
4. Blend Traditional SEO + AI Optimisation (OmniSEO approach)
You should not abandon classic SEO for AI optimisation though, since they complement each other. Many practitioners now follow an OmniSEO model (optimising for both search engines and generative engines). This means you should:- Maintain strong on-page SEO (keywords, internal linking, meta tags) and technical health.
- Layer AI optimisation cues (structured QandA, signals, evidence) on top.
- Monitor both traditional metrics (rankings, organic traffic) and new ones (how often you’re cited by AI).
- Adjust your content based on performance across both channels.
5. Experiment, Monitor, Iterate
AI optimisation is still a developing field. To stay ahead:- Run A/B tests: tweak structures, prompt your content differently, see which versions are more frequently cited.
- Monitor “AI traffic” or referral since some platforms like Perplexity, Gemini or ChatGPT (where citations are clickable) can show you which content get users.
- Use analytics to see whether content cited by AI leads to clickthroughs, reduced bounce, or higher conversions.
- Stay updated with research, e.g. new papers like Generative Engine Optimisation: How to Dominate AI Search (2025) explore empirical methods and biases in AI citation.
Example: How AI Optimisation Might Work in Practice
Let’s take a simplified example: You run a guide on “Sustainable Coffee Production in Vietnam.” You want this guide not only to rank on Google, but to be cited by AI when someone asks, “How is coffee produced sustainably in Vietnam?”Traditional SEO Baseline
- Keyword: “sustainable coffee production Vietnam”, plus secondary keywords (e.g. “shade-grown coffee Vietnam”, “organic coffee Vietnamese farms”).
- Use internal linking to related posts (e.g. “coffee export trends”).
- Use meta title, description, headings.
- Ensure site speed, mobile friendly, schema markup (article schema, FAQ schema).
AI Optimisation / GEO Layer
- Lead with a clear summary: In the first paragraph, answer succinctly: “Sustainable coffee production in Vietnam emphasises shade-grown methods, minimal chemical inputs, soil fertility, water conservation, and fair labour practices.”
- Segment content by roles:
- Definition / overview
- Key sustainability practices (shade-grown, inputs, water)
- Challenges and risks
- Case study: a Vietnamese farm
- Future outlook
- Cues and signals: Use headings like “What is sustainable coffee?”, “Main sustainability practices in Vietnam”, “Case study: XYZ farm in Lam Dong”.
- Evidence and citations: Quote studies, link to government or academic reports. Use data like “X% of farms have adopted shade-grown systems by 2024 (Vietnam Coffee Association)”.
- FAQ schema: Include common user questions e.g. “Why does shade-grown coffee matter in Vietnam?” and answer clearly.
- Update regularly: If a new sustainable practice emerges, add it, so AI sees freshness.





