
What Are SEO AI Agents?
An SEO AI agent is, effectively, an autonomous or semi-autonomous assistant built to handle multiple SEO tasks end-to-end. Some of the key characteristics include:Data Integration and Real-Time Input
These agents pull data from SEO platforms (Search Console, Google Analytics, rank trackers, backlink tools), crawl logs, content repositories, and SERP behaviour, and use them in real time.Intention Understanding
Using NLP (natural language processing) and ML (machine learning), agents infer search intent, semantic relationships, and content gaps beyond simple keyword matching.Decision Support and Prioritisation
More than raw metrics, agents propose or prioritise actions (e.g., “update meta tag here”, “add internal link there”, “merge two pages”, “refresh content”) rather than leaving interpretation to the user.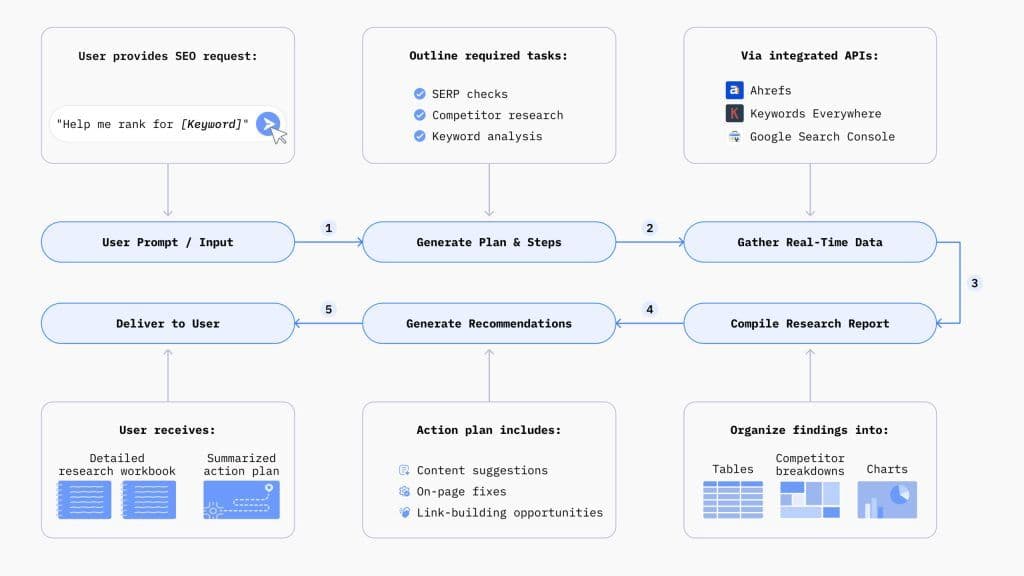
Automation of Execution
In some cases, agents can push changes (for example, schedule content updates, suggest internal linking, flag technical fixes, or generate content briefs).Learning and Feedback Loops
Over time, they refine suggestions based on outcomes (e.g. what updates led to ranking improvements), essentially self-optimising until it becomes better at what it does without needing assistance or fixing from SEO specialists. To borrow a metaphor: whereas a traditional SEO tool is like a map or dashboard (you must plot the route), an AI agent is more like a co-pilot, monitoring the journey and suggesting or even making course corrections automatically.Traditional SEO Tools: Strengths and Limitations
Before exploring the differences, it helps to recap what traditional SEO tools are and how marketers use them. What traditional tools offer:- Keyword research and metrics: Tools such as Ahrefs, SEMrush, Moz, Ubersuggest allow you to see search volume, competition, trends, keyword difficulty, etc.
- Backlink analysis: Checking domain authority, referring domains, anchor texts, toxic links.
- Site audits / technical tools: Crawling for broken links, missing tags, duplicate content, site speed, structured data issues.
- Rank tracking: Monitoring where your pages rank for target keywords over time.
- Content optimisation helpers: Tools that suggest keyword usage, semantic terms, readability improvements, internal link suggestions, etc.
Key Differences: SEO AI Agents vs Traditional Tools
Here is a side-by-side look at how SEO AI agents diverge from traditional tools in practice: Aspect Traditional SEO Tools SEO AI Agents Nature of output Data, charts, alerts, reports Actionable insights, task proposals, automated workflows User involvement Interpretation and prioritisation by user The agent does much of the synthesis and prioritisation Scope Often discrete (keyword tool, audit tool, backlink tool) Multi-domain: audits, content, linking, gap detection, internal linking, etc. Automation Limited (perhaps auto-alerts or scheduled reports) Capable of scheduling changes, sending tasks, flagging emergencies, sometimes executing content updates or link suggestions Learning and feedback Updates require manual re-analysis The agent adapts suggestions based on outcome and user feedback Scale Scaling means more user time or more staff Scaling means more agent coverage without linear human cost Speed and agility Slower (weeks to interpret, test, iterate) Faster (hours or days) Context and nuance Often surface metrics or correlations; more brittle Better at capturing semantic meaning, understanding intent shifts, correlating multifactor signals Because of these differences, SEO AI agents can reduce overhead, speed up iteration, and surface insights that might otherwise stay hidden among tangled datasets. For example, a traditional audit tool might flag that a page’s title tag is too long and a slow loading image exists. But an AI agent can assess the impact, propose a rephrased title, identify which image to compress or replace, and estimate the ranking benefit, all in one workflow.Use Cases: How SEO AI Agents Work in Practice
To make this more concrete, let us consider some practical scenarios where SEO AI agents shine:1. Content Refresh and Gap Detection
Suppose you have a blog post that is slipping in rankings. The agent detects a drop, analyses competitor pages, sees that they cover more up-to-date statistics, additional FAQ sections, or multimedia content. It suggests adding new subheadings, internal linking to newer pages, updating figures, and even generating a content outline for the update.2. Internal Linking Optimisation
Rather than manually auditing internal links, the agent can scan your full site map and content themes, then propose or automatically insert internal links (with appropriate anchor text) to strengthen semantic clusters.3. Keyword Clustering and Topic Modelling
Instead of working with flat keyword lists, the agent groups related keywords by search intent and suggests content themes, content hierarchies, and topic clusters. It might also recommend merging content that overlaps or splitting overly broad pages.4. Real-Time SERP/Competition Monitoring
An agent monitors changes in SERP features (e.g. snippet changes, People Also Ask, AI answer inclusion) and alerts you when competitor content changes that affect your visibility. It can suggest which pages may benefit from new structural changes.5. Technical Health and Automatic Fixes
When technical issues arise (e.g. 404s, canonical conflicts, broken structured data), an AI agent flags them and, where possible, generates the fix proposals (or even pushes code snippets to devs) rather than simply listing the problem.6. GEO Visibility
With the increasing importance of Generative Engine Optimisation (GEO) (i.e. optimising how your content appears in AI-powered search answers like ChatGPT, SGE, Perplexity) some SEO AI agents are also evolving to monitor and optimise for AI answer inclusion (which is beyond traditional SEO focus). This includes tracking how often your brand or site is cited in AI responses, how citation networks relate, and how to shape content to be more “agent-friendly.”Why This Shift Matters — The Strategic Imperative
You might wonder: why go through the trouble of agents if traditional tools largely suffice? The shift is happening for several structural reasons:1. Search is Evolving
With generative AI, answer engines, and AI summaries integrated into SERPs, content is increasingly being consumed via AI interfaces, not just classic link clicks. Optimising merely for traditional ranking may leave you invisible in AI answers.2. Volume and Complexity of Data
As websites grow (thousands of pages, multilingual sites, varied content types), human oversight becomes a bottleneck. Agents scale across complexity that humans cannot keep pace with.3. Speed and Agility Wins
In fast-changing domains, being able to detect and implement SEO changes in hours or days (as opposed to weeks) gives a competitive edge.4. Efficient Resource Use
Instead of hiring more analysts or running multiple tools, you can leverage an agent to take the burden off human teams, letting them focus on more strategic tasks like creativity, brand, and relationships.5. Better Cross-Signal Correlation
Agents are better at correlating signals across datasets (user behaviour, link data, content performance, SERP shifts) to identify high-leverage actions that might be invisible otherwise.Limitations and Risks of SEO AI Agents
An article is not complete without acknowledging caveats. These agents are powerful but not magical. They should not be considered as suitable replacements for marketers or SEO specialists for the following reasons:1. Creativity, Nuance and Brand Voice
AI agents may struggle to replicate brand tone, storytelling, emotional resonance or domain authority as well as a human can. Their content outputs or suggestions may be structurally sound but bland or generic.2. Over-Optimisation Risk
If the agent overly tails suggestions or chases narrow metrics, you might end up with formulaic content or overfitting to algorithms rather than users.3. Dependence and Complacency
Organisations may become too reliant on agents and lose human critical judgment or intuition. Always maintain oversight.4. Data Bias or Errors
Agents are only as good as their data sources. If the underlying analytics, search console data, or crawlers are incomplete or flawed, decisions may be misguided.5. Rapid Change in AI / Algorithmic Behaviour
SEO AI agents must constantly adapt to shifts in search engine algorithms or update how AI models evaluate answers. If the agent’s logic lags behind, it may produce obsolete suggestions.6. Cost and Onboarding
Robust AI agents may come with subscription or infrastructure costs, plus time to train them for your specific site, vertical, and brand.7. Transparency and “Black Box” Concerns
Sometimes, recommendations may emerge without clear rationale, making it hard for users to understand or trust them fully.A Hybrid Strategy: Marrying Agents and Human Expertise
The most forward-thinking approach is not to pick sides, but to integrate. You can use SEO AI agents to handle scale, speed, and breadth while retaining human specialists for strategy, creativity, oversight, and high-stakes decisions. A practical hybrid approach might look like:- Agent for discovery and triage: Let the agent continuously scan your site, surface technical issues, content decay, and gap opportunities.
- Human review and prioritisation: Your SEO or content leads review the agent’s suggestions, approve or edit them, and determine which ones align with brand goals and messaging.
- Execution loop: Agents may even push some lower-risk changes (e.g. meta updates, internal linking) pending human approval. For more sensitive tasks, the human team implements.
- Feedback and learning: Track which agent suggestions actually deliver uplift; feed those results back to refine the agent’s logic or weighting.
How To Leverage SEO AI Agents
If you are considering adopting this new and exciting technology for either personal or commercial use, here are some practical ways you might adopt SEO AI agents effectively:- Select or build a domain-adapted agent: Don’t rely blindly on generic agents. Train or calibrate them to your clients’ verticals, tone, data sources, and success criteria.
- Pilot with existing clients: Start with a controlled pilot: choose a subset of pages or clients, compare agent vs traditional approach, measure uplift, refine.
- Integrate into workflows: Embed agent outputs into your editorial, development, and analytics workflows so that suggestions become part of daily operations—not external extra tools.
- Maintain human oversight and QA: Always review agent recommendations, especially for brand tone, compliance, editorial strategy, and risk control.
- Use agent insights for strategy: The agent’s patterns and suggestions (e.g. clusters, gap analysis, SERP changes) can feed into your macro content calendars, competitive strategy, and campaign planning.
- Educate clients: Help your clients understand the difference between agent-generated optimisations and high-level strategy. Make them comfortable with AI as a tool, not a “black box oracle.”
- Monitor evolving AI/search landscapes: As generative AI, GEO, or answer engine models evolve, keep adapting the agent’s logic, data sources, and metrics.





